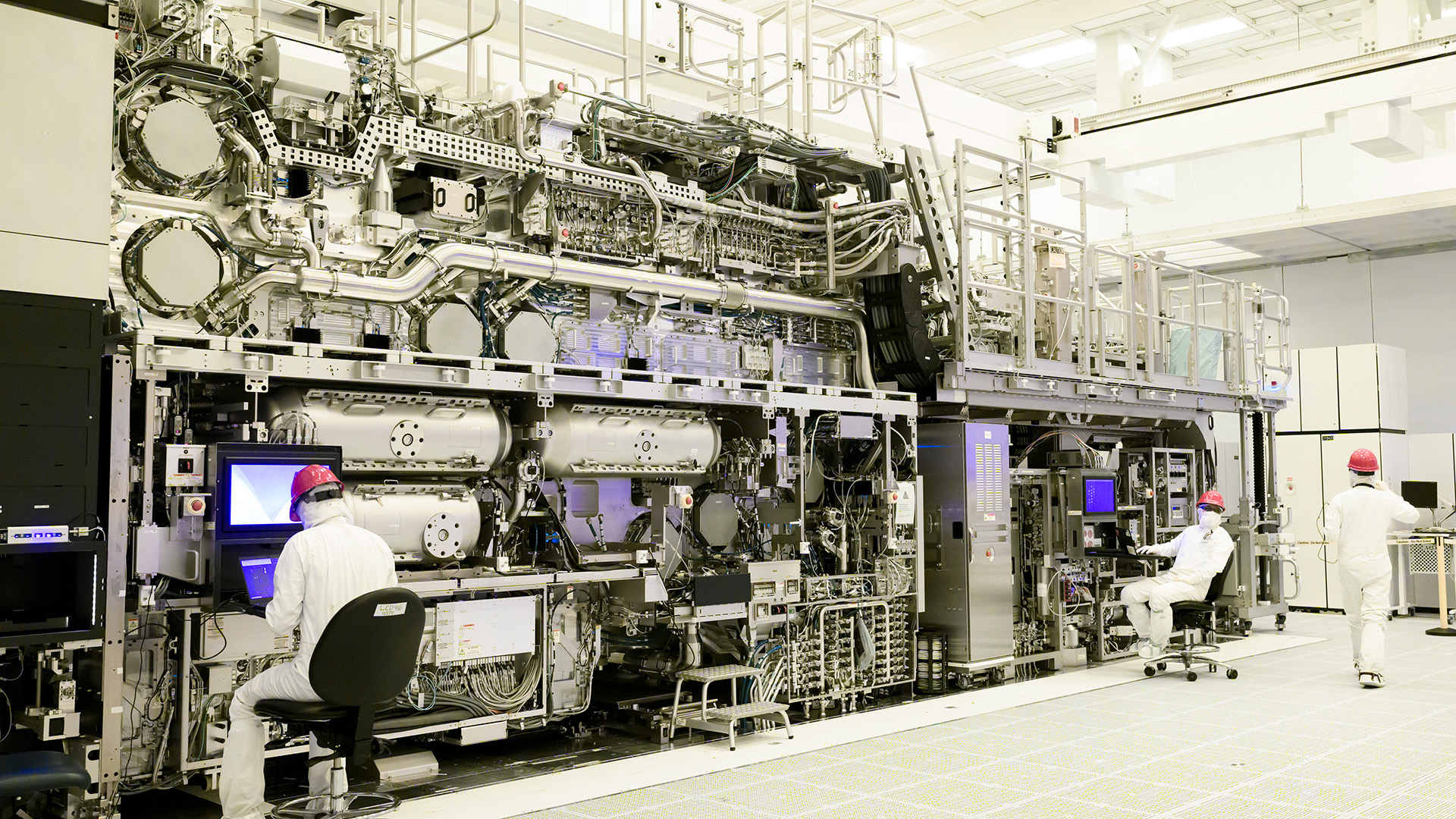
The world's largest chipmaker could flip a kill switch and remotely disable its machines in the event of an invasion
That's one helluva kill switch.
Keep up to date with the most important stories and the best deals, as picked by the PC Gamer team.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Every Friday
GamesRadar+
Your weekly update on everything you could ever want to know about the games you already love, games we know you're going to love in the near future, and tales from the communities that surround them.

Every Thursday
GTA 6 O'clock
Our special GTA 6 newsletter, with breaking news, insider info, and rumor analysis from the award-winning GTA 6 O'clock experts.

Every Friday
Knowledge
From the creators of Edge: A weekly videogame industry newsletter with analysis from expert writers, guidance from professionals, and insight into what's on the horizon.

Every Thursday
The Setup
Hardware nerds unite, sign up to our free tech newsletter for a weekly digest of the hottest new tech, the latest gadgets on the test bench, and much more.

Every Wednesday
Switch 2 Spotlight
Sign up to our new Switch 2 newsletter, where we bring you the latest talking points on Nintendo's new console each week, bring you up to date on the news, and recommend what games to play.

Every Saturday
The Watchlist
Subscribe for a weekly digest of the movie and TV news that matters, direct to your inbox. From first-look trailers, interviews, reviews and explainers, we've got you covered.

Once a month
SFX
Get sneak previews, exclusive competitions and details of special events each month!
TSMC is the world's largest chipmaker, and it produces a massive percentage of the world's advanced computer chips—by some estimates over the past few years, even around 90%. What happens if something were to happen in that part of the world to disturb this chipmaking ability? It'd be catastrophic, of course, but TSMC and its main machine supplier, Dutch company ASML, say the machines wouldn't fall into hostile hands.
Citing people close to the matter, Bloomberg reports both TSMC and ASML have ways to disable the lithographic machines located in Taiwan. This kill switch would be able to be remotely activated, should such a drastic action ever be required.
Officials from the US government have reportedly spoken to both companies about what might happen in the event of an invasion, with ASML reassuring officials it was able to stop the machines from falling into the wrong hands.
The switch applies to the latest EUV machines out of ASML. These are also some of the most complicated, expensive, and sizable chip-making machines around today. The machines themselves have taken years to develop, and even longer to actually implement, though are now responsible for producing the most intricate and powerful computer chips today.
EUV machines demand highly trained specialists, components, resources and more in order to function properly. It's extremely unlikely these machines could function anywhere near as effectively as they do today when disconnected from large parts of the world's economy, if that were to be the case. Yet this is all planning for hypothetical situations, nothing is certain.
Concerns over Taiwan's national security are what have ultimately led to increased spending in chip-making facilities in the US and Europe. The CHIPS Act in the US has agreed to pay huge sums to today's largest chip-making companies, including TSMC, Intel, and Samsung, in order to attract fab facilities to be built, maintained, and expanded on US soil. It seems to be working, too.
Though even by today's optimistic outlooks, a very high percentage of processors will still be manufactured in Taiwan for the foreseeable future.
Keep up to date with the most important stories and the best deals, as picked by the PC Gamer team.
Best CPU for gaming: Top chips from Intel and AMD.
Best gaming motherboard: The right boards.
Best graphics card: Your perfect pixel-pusher awaits.
Best SSD for gaming: Get into the game first.

Jacob earned his first byline writing for his own tech blog, before graduating into breaking things professionally at PCGamesN. Now he's managing editor of the hardware team at PC Gamer, and you'll usually find him testing the latest components or building a gaming PC.