Researchers translate brain waves into scarily accurate images using Stable Diffusion AI
Researchers have been able to use Stable Diffusion models to reconstruct images from human brain waves.

Keep up to date with the most important stories and the best deals, as picked by the PC Gamer team.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Every Friday
GamesRadar+
Your weekly update on everything you could ever want to know about the games you already love, games we know you're going to love in the near future, and tales from the communities that surround them.

Every Thursday
GTA 6 O'clock
Our special GTA 6 newsletter, with breaking news, insider info, and rumor analysis from the award-winning GTA 6 O'clock experts.

Every Friday
Knowledge
From the creators of Edge: A weekly videogame industry newsletter with analysis from expert writers, guidance from professionals, and insight into what's on the horizon.

Every Thursday
The Setup
Hardware nerds unite, sign up to our free tech newsletter for a weekly digest of the hottest new tech, the latest gadgets on the test bench, and much more.

Every Wednesday
Switch 2 Spotlight
Sign up to our new Switch 2 newsletter, where we bring you the latest talking points on Nintendo's new console each week, bring you up to date on the news, and recommend what games to play.

Every Saturday
The Watchlist
Subscribe for a weekly digest of the movie and TV news that matters, direct to your inbox. From first-look trailers, interviews, reviews and explainers, we've got you covered.

Once a month
SFX
Get sneak previews, exclusive competitions and details of special events each month!
Imagine having the ability to recall your memories with near perfect precision. As we move into an ever more AI-centric future, that dream looks set to come true. With researchers now having used Stable Diffusion to reconstruct pretty damn accurate, high resolution images by reading human brain waves, we could one day be pulling up images from the annals of our minds without having taken a single photograph.
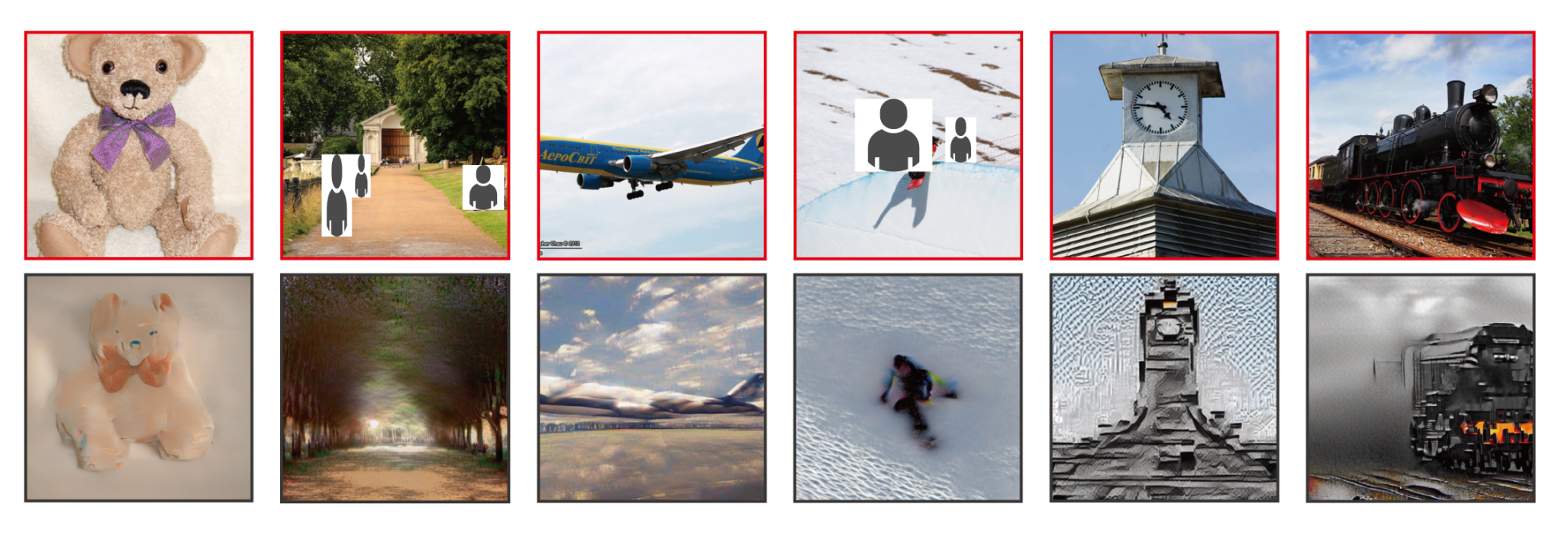
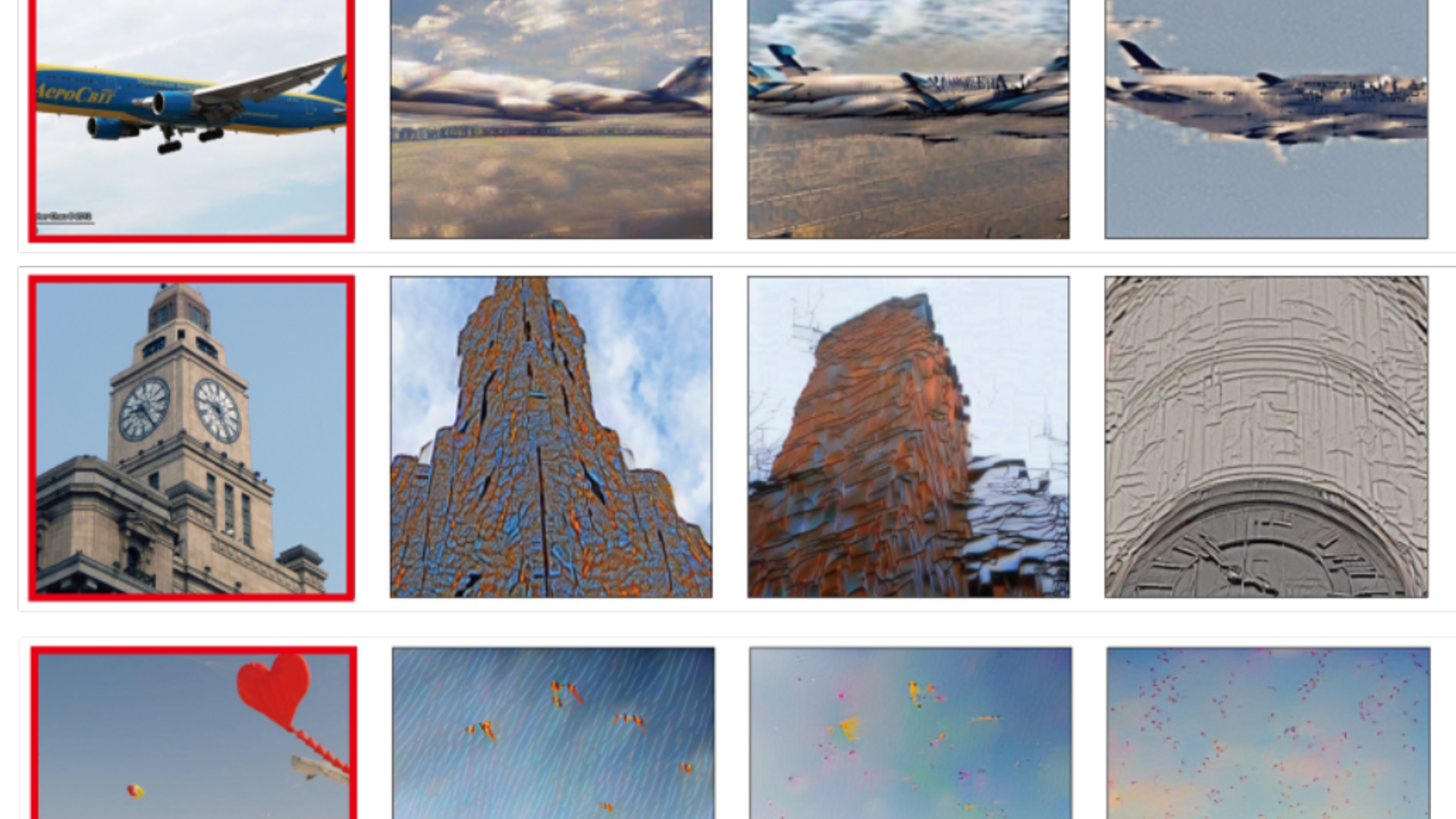
Researchers Yu Takagi and Shinji Nishimoto, from the Graduate School of Frontier Biosciences at Osaka University, recently wrote a paper outlining how it's possible to reconstruct high res images (PDF) using latent diffusion models, by reading human brain activity gained from functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), "without the need for training or fine-tuning of complex deep generative models" (via Vice).
Considering we don't fully understand how the underlying translation happens in the brain, the results from this research are incredible. The fact Takagi and Nishimoto were able to coax high resolution images from the latent space using human brain waves is astonishing.
Alright, they say high resolution, but we're talking 512 x 512 pixels. Still, it's a darn sight better than the 256p the competition had managed, and with a much higher "semantic fidelity", too. In other words, the translations are actually vaguely recognisable, and representative of the original images participants had been shown.
Previous studies involved "training and possibly fine-tuning of generative models, such as GANs, with the same dataset used in the fMRI experiments", the researchers explain. It's challenging as these generative models are not only awkward as heck to work with, but the training material is super limited. It looks like the Osaka researchers have been able to circumvent these limitations using Stable Diffusion, and the results are looking genuinely impressive.
We've all seen the Black Mirror episode. The Entire History of You is a terrifying look into a future in which an implant records our daily life so we can later put every moment under intense scrutiny and ruin our relationships.
But before you consign the idea of using AI for visual recall to the dystopian segment of your brainhole, think of the practical uses! We could one day see nonverbal people, or paralysed people who can't simply snap a pic of something to show later, able to show us exactly what they're thinking of by running their brain waves through an artificial intelligence.
Keep up to date with the most important stories and the best deals, as picked by the PC Gamer team.

Best gaming PC: The top pre-built machines from the pros
Best gaming laptop: Perfect notebooks for mobile gaming
As one of the first studies (if not the first) to use diffusion models in this way, it may at least help to paint such algorithms in a better light. Stable Diffusion has come under fire of recent—at least in the art space. Rightly so when some diffusion models scrape the internet and regurgitate the front page of ArtStation, only to be used for some lazy party's own financial gain.
But if the data is used right, and the ease of training these models can benefit the field of accessibility so people can give accurate representations of their own inner worlds, and communicate in new ways, I'm all for it.

Having been obsessed with game mechanics, computers and graphics for three decades, Katie took Game Art and Design up to Masters level at uni and has been writing about digital games, tabletop games and gaming technology for over five years since. She can be found facilitating board game design workshops and optimising everything in her path.